Disinflation - One Step Forward, Two Steps Back
October 11, 2022
Read Time 2 MIN
EM Disinflation Progress
Well, to be more precise, it’s one country forward and two countries back. Brazil is on a roll, with headline annual inflation easing to 7.17% (pretty much as expected) in September. Brazil’s disinflation chart looks really great (see below), with early and aggressive rate hikes, fiscal measures, and the currency’s solid performance contributing to the disinflation process. But back in Central Europe, Hungary’s inflation surged to eye-popping 20.1% year-on-year (a meaningful upside surprise), and Czech annual inflation unexpectedly re-accelerated to 18%.
End of EM Tightening Cycles
An interesting twist here is that all three countries that released their September inflation prints today (Brazil, Hungary, and the Czech Republic) signaled the end of their tightening cycles. But as far as we can tell, only the Brazilian central bank is on more or less solid ground - both fundamentally and also having raised its benchmark rate by 1175bps since early 2021. The Hungarian national bank made an impressive catch-up effort in the past weeks - the policy rate is now 13% (almost as high as Brazil’s). The question is whether new instruments would be effective in mopping up liquidity. We also keep an eye on Hungary’s efforts to correct the pre-election fiscal “splurge.” The Czech national bank’s bet is that weaker growth would reduce inflation pressures going forward and that it can rely on currency interventions to offset external price pressures. Would this work before inflation expectations become un-anchored?
Global Price Pressures
Emerging markets (EM) and global inflation trends are at the center of discussions during the International Monetary Fund (IMF) annual meetings in Washington, DC, where we are spending this week. What elements of inflation can the U.S. Federal Reserve and other major central banks actually control? How much more monetary authorities want to do in the current environment - do we need a recession to unwind some (or most?) of price pressures? Is there a risk that major central banks will stop tightening prematurely and will be forced to re-engage later in 2023? Stay tuned!
Chart at a Glance: Brazil Disinflation - Looking Good!
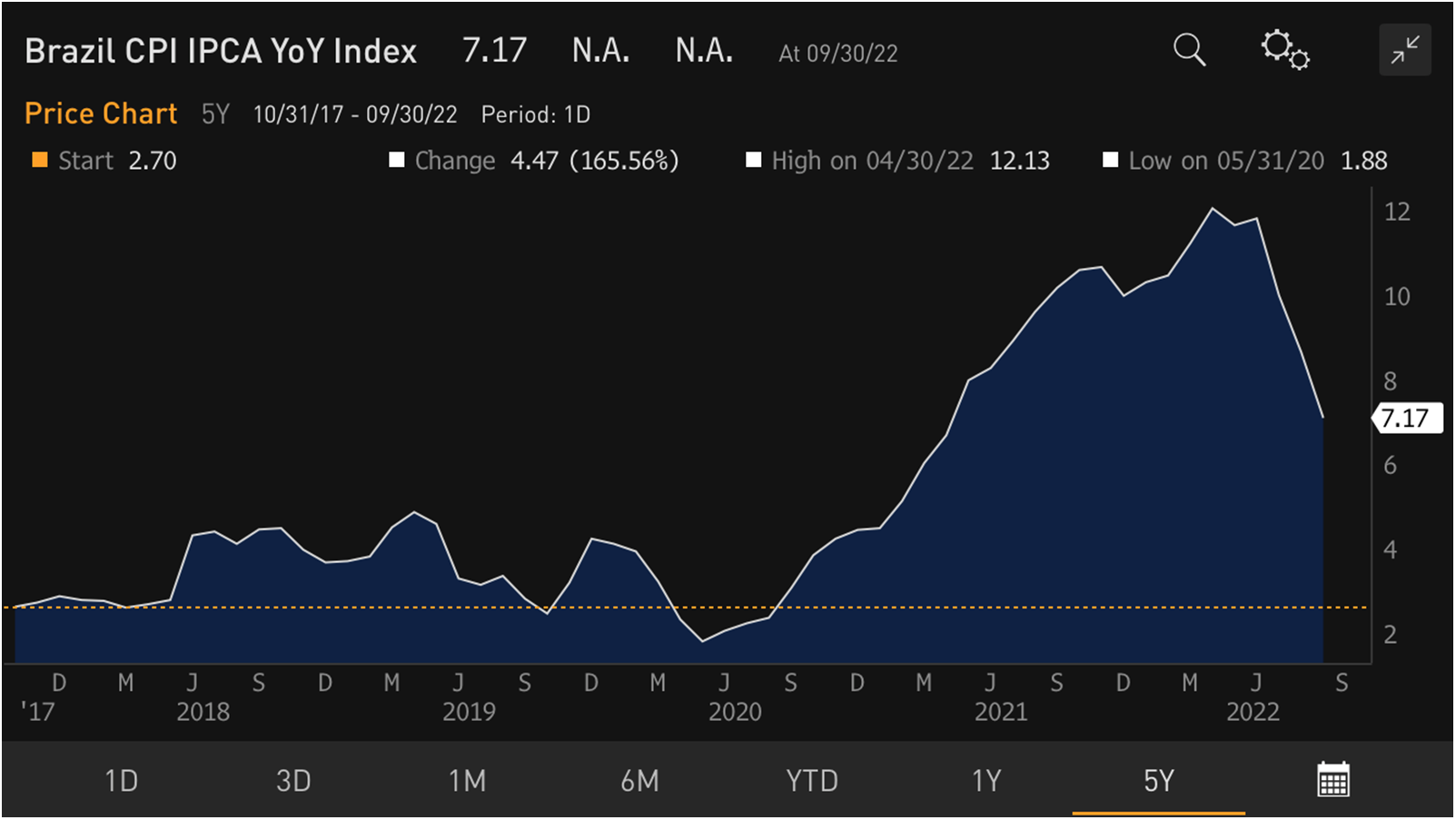
Source: Bloomberg LP
Follow Us
PMI – Purchasing Managers’ Index: economic indicators derived from monthly surveys of private sector companies. A reading above 50 indicates expansion, and a reading below 50 indicates contraction; ISM – Institute for Supply Management PMI: ISM releases an index based on more than 400 purchasing and supply managers surveys; both in the manufacturing and non-manufacturing industries; CPI – Consumer Price Index: an index of the variation in prices paid by typical consumers for retail goods and other items; PPI – Producer Price Index: a family of indexes that measures the average change in selling prices received by domestic producers of goods and services over time; PCE inflation – Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index: one measure of U.S. inflation, tracking the change in prices of goods and services purchased by consumers throughout the economy; MSCI – Morgan Stanley Capital International: an American provider of equity, fixed income, hedge fund stock market indexes, and equity portfolio analysis tools; VIX – CBOE Volatility Index: an index created by the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE), which shows the market's expectation of 30-day volatility. It is constructed using the implied volatilities on S&P 500 index options.; GBI-EM – JP Morgan’s Government Bond Index – Emerging Markets: comprehensive emerging market debt benchmarks that track local currency bonds issued by Emerging market governments; EMBI – JP Morgan’s Emerging Market Bond Index: JP Morgan's index of dollar-denominated sovereign bonds issued by a selection of emerging market countries; EMBIG - JP Morgan’s Emerging Market Bond Index Global: tracks total returns for traded external debt instruments in emerging markets.
The information presented does not involve the rendering of personalized investment, financial, legal, or tax advice. This is not an offer to buy or sell, or a solicitation of any offer to buy or sell any of the securities mentioned herein. Certain statements contained herein may constitute projections, forecasts and other forward looking statements, which do not reflect actual results. Certain information may be provided by third-party sources and, although believed to be reliable, it has not been independently verified and its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Any opinions, projections, forecasts, and forward-looking statements presented herein are valid as the date of this communication and are subject to change. The information herein represents the opinion of the author(s), but not necessarily those of VanEck.
Investing in international markets carries risks such as currency fluctuation, regulatory risks, economic and political instability. Emerging markets involve heightened risks related to the same factors as well as increased volatility, lower trading volume, and less liquidity. Emerging markets can have greater custodial and operational risks, and less developed legal and accounting systems than developed markets.
All investing is subject to risk, including the possible loss of the money you invest. As with any investment strategy, there is no guarantee that investment objectives will be met and investors may lose money. Diversification does not ensure a profit or protect against a loss in a declining market. Past performance is no guarantee of future performance.
PMI – Purchasing Managers’ Index: economic indicators derived from monthly surveys of private sector companies. A reading above 50 indicates expansion, and a reading below 50 indicates contraction; ISM – Institute for Supply Management PMI: ISM releases an index based on more than 400 purchasing and supply managers surveys; both in the manufacturing and non-manufacturing industries; CPI – Consumer Price Index: an index of the variation in prices paid by typical consumers for retail goods and other items; PPI – Producer Price Index: a family of indexes that measures the average change in selling prices received by domestic producers of goods and services over time; PCE inflation – Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index: one measure of U.S. inflation, tracking the change in prices of goods and services purchased by consumers throughout the economy; MSCI – Morgan Stanley Capital International: an American provider of equity, fixed income, hedge fund stock market indexes, and equity portfolio analysis tools; VIX – CBOE Volatility Index: an index created by the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE), which shows the market's expectation of 30-day volatility. It is constructed using the implied volatilities on S&P 500 index options.; GBI-EM – JP Morgan’s Government Bond Index – Emerging Markets: comprehensive emerging market debt benchmarks that track local currency bonds issued by Emerging market governments; EMBI – JP Morgan’s Emerging Market Bond Index: JP Morgan's index of dollar-denominated sovereign bonds issued by a selection of emerging market countries; EMBIG - JP Morgan’s Emerging Market Bond Index Global: tracks total returns for traded external debt instruments in emerging markets.
The information presented does not involve the rendering of personalized investment, financial, legal, or tax advice. This is not an offer to buy or sell, or a solicitation of any offer to buy or sell any of the securities mentioned herein. Certain statements contained herein may constitute projections, forecasts and other forward looking statements, which do not reflect actual results. Certain information may be provided by third-party sources and, although believed to be reliable, it has not been independently verified and its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Any opinions, projections, forecasts, and forward-looking statements presented herein are valid as the date of this communication and are subject to change. The information herein represents the opinion of the author(s), but not necessarily those of VanEck.
Investing in international markets carries risks such as currency fluctuation, regulatory risks, economic and political instability. Emerging markets involve heightened risks related to the same factors as well as increased volatility, lower trading volume, and less liquidity. Emerging markets can have greater custodial and operational risks, and less developed legal and accounting systems than developed markets.
All investing is subject to risk, including the possible loss of the money you invest. As with any investment strategy, there is no guarantee that investment objectives will be met and investors may lose money. Diversification does not ensure a profit or protect against a loss in a declining market. Past performance is no guarantee of future performance.