China – Bucking the Trend?
March 01, 2022
Read Time 2 MIN
Summary
China’s latest PMIs shows that the stimulus started to work its way through the economy. Details call for continuing support, and the new official growth target will signal how much more authorities are willing to disburse.
CHINA AND GEOPOLITICAL RISKS
Tectonic shifts that are currently taking place in geopolitics and global markets might have placed China in a unique position as regards its growth outlook. It’s not just about geography and proximity to the Russia/Ukraine war – albeit this is an important consideration for emerging markets outside of EMEA. The 2021 growth hiccups and regulatory overreaches forced Chinese authorities to re-deploy pro-growth accommodative policies in a situation when many emerging markets (EM) were aggressively tightening and developed markets (DM) were moving towards policy normalization. Yes, China’s “new” stimulus is still very measured and mostly targeted (there were some small blanket rate cuts), but China’s big advantage is that upside inflation pressures are nowhere to be seen – unlike pretty much the rest of the world – and this leaves plenty of room for additional policy support (without losing sleep about prices).
CHINA DOMESTIC RECOVERY
China’s real estate sector is not yet out of the woods – the preliminary home sales numbers for January-February looked weak. However, the latest domestic activity gauges – both official and Caixin Purchasing Managers Indices (PMI)1– show that the past stimulus started to work its way through the economy. All headline February PMIs surprised to the upside, including such forward-looking components as new orders (50.7, see chart below)). The non-manufacturing PMI was also better than expected (51.6), with rebounds both in services and construction. The latter might be due to the renewed support for infrastructure, especially on the fiscal side.
CHINA STIMULUS AND GROWTH TARGET
PMI details tell us that China’s stimulus should continue in the coming months. Many sub-indices are still “hugging” the expansion/contraction border, and some - like the small company PMI – remain “underwater” (i.e. below 50.0). Exactly how much additional support we are talking about will become clearer after the forthcoming meetings of the National People’s Congress and Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference, which should set the official growth target. China’s consensus growth forecast for 2022 was cut a lot in the fall of last year, but it remained stable around 5.2% since mid-December. Can China re-affirm its status as an independent global growth driver? Stay tuned!Chart at a Glance: China Activity Gauges – Tentative Improvement
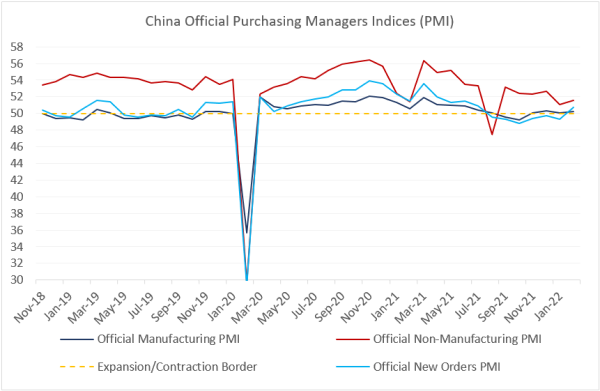
Source: Bloomberg LP
Related Topics
Related Insights
February 26, 2024
January 04, 2024
October 27, 2023
PMI – Purchasing Managers’ Index: economic indicators derived from monthly surveys of private sector companies. A reading above 50 indicates expansion, and a reading below 50 indicates contraction; ISM – Institute for Supply Management PMI: ISM releases an index based on more than 400 purchasing and supply managers surveys; both in the manufacturing and non-manufacturing industries; CPI – Consumer Price Index: an index of the variation in prices paid by typical consumers for retail goods and other items; PPI – Producer Price Index: a family of indexes that measures the average change in selling prices received by domestic producers of goods and services over time; PCE inflation – Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index: one measure of U.S. inflation, tracking the change in prices of goods and services purchased by consumers throughout the economy; MSCI – Morgan Stanley Capital International: an American provider of equity, fixed income, hedge fund stock market indexes, and equity portfolio analysis tools; VIX – CBOE Volatility Index: an index created by the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE), which shows the market's expectation of 30-day volatility. It is constructed using the implied volatilities on S&P 500 index options.; GBI-EM – JP Morgan’s Government Bond Index – Emerging Markets: comprehensive emerging market debt benchmarks that track local currency bonds issued by Emerging market governments; EMBI – JP Morgan’s Emerging Market Bond Index: JP Morgan's index of dollar-denominated sovereign bonds issued by a selection of emerging market countries; EMBIG - JP Morgan’s Emerging Market Bond Index Global: tracks total returns for traded external debt instruments in emerging markets.
The information presented does not involve the rendering of personalized investment, financial, legal, or tax advice. This is not an offer to buy or sell, or a solicitation of any offer to buy or sell any of the securities mentioned herein. Certain statements contained herein may constitute projections, forecasts and other forward looking statements, which do not reflect actual results. Certain information may be provided by third-party sources and, although believed to be reliable, it has not been independently verified and its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Any opinions, projections, forecasts, and forward-looking statements presented herein are valid as the date of this communication and are subject to change. The information herein represents the opinion of the author(s), but not necessarily those of VanEck.
Investing in international markets carries risks such as currency fluctuation, regulatory risks, economic and political instability. Emerging markets involve heightened risks related to the same factors as well as increased volatility, lower trading volume, and less liquidity. Emerging markets can have greater custodial and operational risks, and less developed legal and accounting systems than developed markets.
All investing is subject to risk, including the possible loss of the money you invest. As with any investment strategy, there is no guarantee that investment objectives will be met and investors may lose money. Diversification does not ensure a profit or protect against a loss in a declining market. Past performance is no guarantee of future performance.
1We believe PMIs are a better indicator of the health of the Chinese economy than the gross domestic product (GDP) number, which is politicized and is a composite in any case. The manufacturing and non-manufacturing, or service, PMIs have been separated in order to understand the different sectors of the economy. These days, we believe the manufacturing PMI is the number to watch for cyclicality.
PMI – Purchasing Managers’ Index: economic indicators derived from monthly surveys of private sector companies. A reading above 50 indicates expansion, and a reading below 50 indicates contraction; ISM – Institute for Supply Management PMI: ISM releases an index based on more than 400 purchasing and supply managers surveys; both in the manufacturing and non-manufacturing industries; CPI – Consumer Price Index: an index of the variation in prices paid by typical consumers for retail goods and other items; PPI – Producer Price Index: a family of indexes that measures the average change in selling prices received by domestic producers of goods and services over time; PCE inflation – Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index: one measure of U.S. inflation, tracking the change in prices of goods and services purchased by consumers throughout the economy; MSCI – Morgan Stanley Capital International: an American provider of equity, fixed income, hedge fund stock market indexes, and equity portfolio analysis tools; VIX – CBOE Volatility Index: an index created by the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE), which shows the market's expectation of 30-day volatility. It is constructed using the implied volatilities on S&P 500 index options.; GBI-EM – JP Morgan’s Government Bond Index – Emerging Markets: comprehensive emerging market debt benchmarks that track local currency bonds issued by Emerging market governments; EMBI – JP Morgan’s Emerging Market Bond Index: JP Morgan's index of dollar-denominated sovereign bonds issued by a selection of emerging market countries; EMBIG - JP Morgan’s Emerging Market Bond Index Global: tracks total returns for traded external debt instruments in emerging markets.
The information presented does not involve the rendering of personalized investment, financial, legal, or tax advice. This is not an offer to buy or sell, or a solicitation of any offer to buy or sell any of the securities mentioned herein. Certain statements contained herein may constitute projections, forecasts and other forward looking statements, which do not reflect actual results. Certain information may be provided by third-party sources and, although believed to be reliable, it has not been independently verified and its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Any opinions, projections, forecasts, and forward-looking statements presented herein are valid as the date of this communication and are subject to change. The information herein represents the opinion of the author(s), but not necessarily those of VanEck.
Investing in international markets carries risks such as currency fluctuation, regulatory risks, economic and political instability. Emerging markets involve heightened risks related to the same factors as well as increased volatility, lower trading volume, and less liquidity. Emerging markets can have greater custodial and operational risks, and less developed legal and accounting systems than developed markets.
All investing is subject to risk, including the possible loss of the money you invest. As with any investment strategy, there is no guarantee that investment objectives will be met and investors may lose money. Diversification does not ensure a profit or protect against a loss in a declining market. Past performance is no guarantee of future performance.
1We believe PMIs are a better indicator of the health of the Chinese economy than the gross domestic product (GDP) number, which is politicized and is a composite in any case. The manufacturing and non-manufacturing, or service, PMIs have been separated in order to understand the different sectors of the economy. These days, we believe the manufacturing PMI is the number to watch for cyclicality.

